
e-Invoicing | e-Invoice under GST | ERP & e-Invoicing
e-Invoicing is a major reform towards Digital India. e-Invoicing is the digitalization of the Invoices for goods and services provided by companies. The Economic Times has reported that “The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) Wednesday notified that e-invoicing will be mandatory for the business to business (B2B) transactions for taxpayers having turnover of over Rs. 100 crore from January 1, 2021”. In this article, we are going to discuss in-depth about e-Invoicing initiative in India, objectives, benefits, procedures, and how to make your organization ready for e-Invoicing
What is e-Invoicing?
An e-invoice enables a fully automated flow of invoices, right from the time invoice is generated in one company, to the way it is transmitted, how it is processed, and finally received by the concerned parties, everything happens online electronically.
“E-Invoicing” or “Electronic Invoicing” System has been implemented by the Goods & Services Tax (GST) Council of India with effect from October 2020 for taxpayers with aggregate turnover of more than ₹ 500 CR in the previous Financial Year (FY).
E-Invoicing is the system by which all B2B Invoices generated by a company are electronically validated on the GSTN Portal (Goods and Services Tax Network) and the invoice information is made available in real-time, to both, the Goods & Services Tax Portal as well as the E-way Bill Portal
India has adopted the ‘clearance’ model of e-invoicing. In the ‘clearance’ model, an invoice has to be reported and ‘cleared’ from a government-designated portal before issuing to the buyer. This is where the Invoice Registration Portal (“IRP”), IRN (“Invoice Reference Number”) QR code (Quick Response code) will come into the picture. We will discuss more of this in the following sections.
What is the objective of e-Invoicing?
GST Council observed that businesses submitted invoices in their respective formats, generated by their ERP/Billing/Accounting software. Although invoices contained more or less the same information, other computer systems couldn’t read and understand invoices completely. For example, an Invoice generated in “SAP” cannot be read by a machine using “Tally”. Therefore, it felt a dire need for standardization and automation of invoices, which could eliminate the need for manual data entry of invoices and the possibility of human errors creeping into the system.
e-Invoice or e-Invoicing system is conceived & developed in consultation with the Institute of Chartered Accounts India (ICAI) and trade/industry bodies with the following objectives:
- Introduce standard e-Invoice Format (schema) across industries & businesses in India
- Achieve machine readability and seamless exchange of data
- Enable uniform interpretation of invoice data
- Ensure complete interoperability among various software and tax systems
With the advent of an e-invoice, a standardized document will be shared by sellers with buyers or banks, or other third parties, in a machine-readable format, which can be transmitted easily to other systems
Which documents are valid for e-Invoicing?
The following type of Invoices will be covered under e-Invoicing:
- Invoices by Supplier
- Credit Note by Supplier
- Debit notes by the recipient
- Reverse Charge Invoice
- Other Documents specified by Law
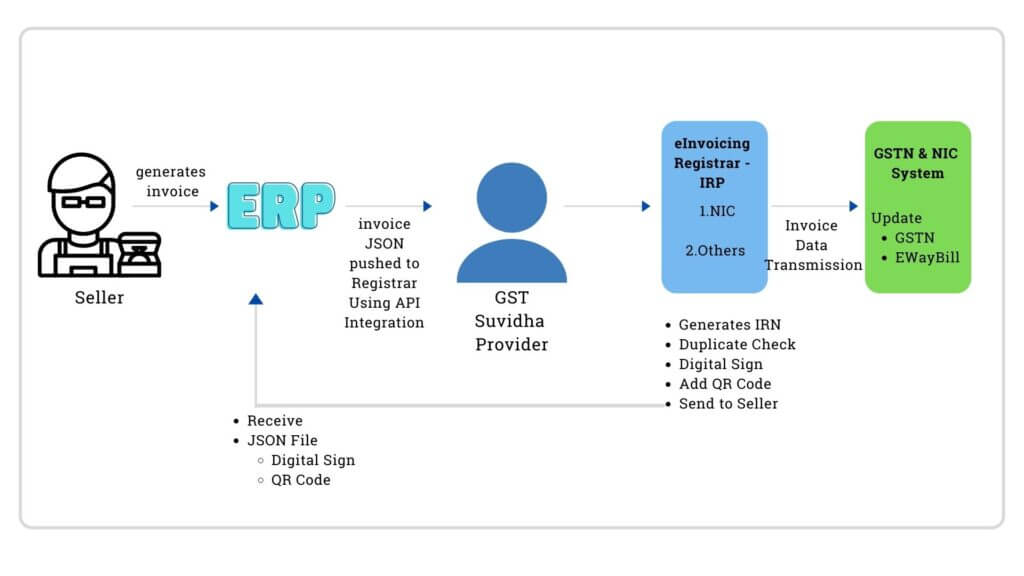
How will the e-Invoicing model in India work?
Following processes will be carried out for the e-Invoicing model in India
Step 1: Companies will generate the B2B Invoices using their respective ERP/Accounting/Billing Software as before.
Step 2: An electronic file is prepared using the prescribed schema in JSON format and sent to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP Portal)
Step 3: IRP will generate a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN**), digitally sign the eInvoice and also generate a Quick Response Code (QR Code) which contains important details of the e-Invoice and return it to the seller.
Step 4: IRP will send the signed e-invoice to the seller’s email provided in the e-invoice.
Step 5: Invoice details will be auto-populated in the GSTN & EWay Bill System
What information is required to generate an e-Invoice in GST?
- Supplier GSTIN, Supplier’s invoice number and, Financial year (YYYY-YY)
- Details of supplier & consignee
- Type of supply
- If it is B2B or B2C
- If it attracts RCM
- If it attracts TDS/TCS
- If it is an Export, Supply made to SEZ or Deemed export
- Details of supply
- Authorization by designed authority
What is the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)?
The Invoice Registration Portals perform the role of Registrar who assign Invoice Reference Numbers (IRN) to each invoice/credit note/debit note. Only invoices having authorized IRN will be considered valid as per law.
IRP is responsible for performing the following tasks:
- Generate hash/IRN: Generate IRN for invoices as per specified format & parameters
- Validate hash/IRN for invoices: If the taxpayer has generated hash, validate compliance with the prescribed format
- Check for Duplicates: Check hash/IRN for duplication by comparing central depository information
- Digital Sign: IRP will digitally sign invoices using a Private Key and dispatch the signed JSON file to the supplier
- Generate QR code: IRP generates QR codes for authenticated invoices. This makes it easy to verify/print/view/access information on mobile devices.
- Dispatch invoice via e-mail: Send Validated invoices to the seller’s email address
- Integration with GST and E-Way Bill system: Automatically share the Invoice details with the GST system and update GSTR-1 (of the seller). Auto-populates information in the E-Way Bill system (if required).
What is the Invoice Reference Number (IRN)?
Invoice Reference Number (IRN) is a unique identifier (also known as hash) comprising of 64 characters and is generated by the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) for every invoice raised by the supplier. The 64 characters include a combination of GSTIN number of Supplier along with Document Type, Document Number and Financial Year. You can generate an IRN by using API integration with the e-invoice portal/IRP or via GST Suvidha Provider
What information does Quick Response Code (QR Code) contain?
The QR code shall comprise of the following details
- GSTIN of supplier
- GSTIN of Recipient
- Invoice number as given by Supplier
- Date of the generation of invoice
- Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
- Number of line items.
- HSN Code of the main item (the line item having the highest taxable value)
- Unique Invoice Reference Number (hash)
e-Invoicing and ERP Integration
Integrating your company ERP using an API framework for directly connecting with the GST Suvidha Provider (GSP) has a lot of advantages.
- Create Invoices within ERP: Businesses can create eInvoice/IRN from within the ERP itself and send it to the IRP in real-time for processing. The response will also be captured directly into ERP.
- Automatic Data Transfer: ERP Integration enables the automation of information flow from ERP to IRP. This eliminates manual efforts and chances of compliance errors. It also reduces the time required to upload data from the ERP.
- Data Validation: IRP accepts the File in JSON format and checks for any errors in the initial stages and sends it back for corrections. Thus, it prevents the cancellations of invoices
- Data Segregation: A GSP enables you to define & manage multiple PANs, GSTINs, and branches by providing unique owner IDs at each hierarchical level. You can send data out for different PANs or GSTINs using the same integration.
Although ERP configuration using API-based integration involves relatively higher costs and efforts it will be a benefit because:
- e-invoice/IRN can be generated in real-time.
- e-invoices can be directly canceled using ERP.
- Eliminate manual effort required to generate e-invoices.
- Zero chances of errors since there is no human intervention
What Changes/modifications are required in ERP to become ready for e-Invoicing?
To become ready for e-Invoicing, you will have to make some changes to ERP and ensure that a unique document number is being assigned to every invoice being generated in the company. You will also have to make provisions for the following.:
1. Prepare JSON File : ERP Software should be capable to generate the JSON file of the Invoice that has to be uploaded to the IRP. It should also enable printing the QR Code & IRN number on the invoices validated by the IRP.
2. Transaction Classification : ERP Software will have to make provision to classify a transaction into the following categories:
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Business-to-Consumer(B2C)
- Business-to-Government (B2G)
- Export
- Supply through e-commerce operator
- Supply liable to reverse charge
ERP should also be able to capture details required as per Part A of the e-way bill
3. ERP Integration & Data Exchange using APIs : ERP Software will have to enable data exchange using the APIs for :
- Authentication
- Generate IRN
- Cancel IRN
- Get e-invoice by IRN
- Get GSTIN details
4. Linking Accounts Payables & Receivables : The ERP Software will have to incorporate a method to link the invoices to the accounts receivables and accounts payables modules. You will be not able to avail of Input Tax Credit if payments are not completed within 180 days of the date of invoice. ERP will enable setting up automated reminders for payments on time.
5. Tracking Amendments/Cancellation of Invoices : Remember Invoices can be canceled only within a period of 24 hours from uploading to the portal. ERP Software has to become equipped to keep a track of canceled invoices and canceled E-way Bill numbers. This will prevent the same number from being used again while preparing e-Invoices. ERP should provide a mechanism to link the amended invoices to the original documents.
6. Storage of invoices : The Invoice Registration Portal does not have a provision to store invoices. ERP software must ensure storage of validated e-Invoices with relevant details for quick reference at a future date
What are the Benefits of eInvoicing?
Let us now see the benefits of e-Invoicing in India for Businesses as well as the Government.
e-Invoicing Benefits for Businesses
- Standardization: One single standard Invoice Format designed for all businesses. It can be directly transmitted from one financial system to another.
- Eliminate paperwork: No need to prepare invoices in varied formats & elimination of the possibility of data-entry errors
- Easier Compliance: Real-time, auto-population of invoice details in GST returns for supplier & buyers and Simultaneous generation of E-way bill, wherever required
- Automation: Auto-generation of Sales and Purchase Registers (ANX-1 and ANX-2).
- Real-Time Information: Information will become available to all parties in almost real-time or near real-time.
- Easier Data Reconciliation: Single source of information will reduce efforts and time taken for reconciliation. This will reduce the possibility of disputes among parties and ensure faster payment cycles.
- Speed & Efficiency: All the above-mentioned points will help enhance Speed & Efficiency of Business
e-Invoicing Benefits for Government
- Allows complete traceability of B2B invoices which helps curbs tax evasion
- Brings efficiency in tax administration
Summary
e-Invoicing is going to be mandatory for companies with a turnover of more than 100 Crores from January 2021. It is an effective measure to introduce standardization, interoperability, easier compliance. ERP Software will prove to be an effective tool for the smooth, easy, and accurate implementation of e-Invoicing in your company.
Request a Demo of Spectrum ERP Software
Contact us for more information

