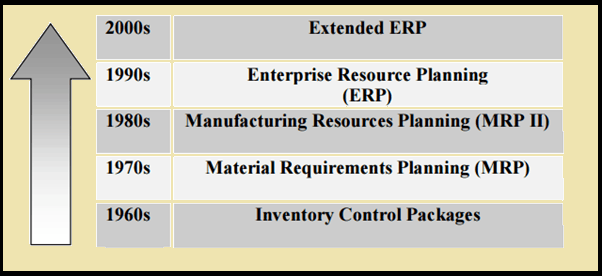
Steps in the Evolution of ERP
ERP is one of the major part of an industry and using it correctly will help in making the industry more efficient and optimize their supply chain, however ERP didn’t came to be suddenly, evolution of ERP occurred in a timely manner and it evolved as time passed and finally came into the form we know.
It started in the form of a inventory control system in 1960. Looking at how beneficial a computer based database is for industries and in response to Toyota manufacturing program Joseph Orlicky developed material requirements planning (MRP) in 1964. The first company to use MRP was Black & Decker in 1964.
Material requirements planning further evolved to manufacturing resource planning in 1980s also called MRPII. While MRP was primarily concerned with materials, MRPII was concerned with the integration of all aspects of the manufacturing process, including materials, finance and human relations. This then further evolved and finally in 1990’s Gartner group chipped in the term ERP. Now on the 21st century ERP is also evolved and ERPII has came into existence.
MRP(Material requirements planning)
Evolution of ERP began with MRP. MRP stands for material requirement planning. It was developed by engineer Joseph Orlicky. MRP is a production planning and inventory control system that was in use extensively before ERP came in the picture. MRP helps in integrating data from production schedules from inventory and Bill of Materials (BOM) to calculate purchasing and shipping costs and schedules for the parts required to build a product. The first computerized MRP system was tested successfully by Black & Decker in 1964.
MRP is generally used for 3 functions:-
- 1. MRP helps in ensuring that right materials are available for production with right quantity to avoid shortages.
- 2. MRP helps in reducing waste by maintaining lowest possible materials and product levels in stock.
- 3. An MRP system helps plan manufacturing functions, delivery schedules and purchasing.
The main shortcoming of an MRP system is Data Integrity. For successful material requirements planning the data fed in the system must be accurate or it can cause serious production and stock errors.
MRP 2.0(Manufacturing resource planning)
Manufacturing resource planning or MRP 2.0 is an integrated system used by businesses, it is an upgrade from manufacturing requirement planning, it allows additional data such as employee and financial needs. The system is designed to centralize, integrate and process information for effective decision making in scheduling, design engineering, inventory management and cost control in manufacturing.
It is a computer based system that can create detail production schedules using real time data to coordinate the arrival of component materials with machine and labor availability.
MRP 2.0 is widely used in industries today by itself but it can also be used as a module of more extensive ERP systems.
ERP(Enterprise resource planning)
ERP stands for enterprise resource planning. All business have different systems, like financials to watch the accounts, production to watch productivity, inventory to keep tracks of your supplies, sales to keep in bringing the customers, services to look into your customer needs and purchasing to shop for your product, now data of some of these systems are needed for the functioning of other systems like data of sales system can be needed for production system which can be needed for finance. Various interfaces are used to transfer data from sales to manufacturing and than from manufacturing to financial. This can reduce the efficiency of the company and can cause data loss too.
The function of ERP is to create a common database serving in multiple functional areas so whenever data of one system is needed for other it can be attained easily. An ERP system seeks to streamline business operations by integrating the data and refining the processes required to operate an organization. ERP is business solution software that integrates and automates the data management of a company’s business processes.
ERP 2.0(Enterprise resource planning II)
The current step in the evolution of ERP is ERP 2.0. ERP 2.0 comes with all the functions as ERP with improvement in functionality associated with supply chain management, supplier relationship management and customer relationship management. All of these tend to encourage collaboration with entities or companies outside of the original enterprise that implemented ERP.
ERP II can enable access to information by those outside the company or original entity, e.g., a manufacturing plant that allows access to planning information by another plant or its customers. Software that allows access by those outside the company has more stringent security plus design to avoid access to certain company information.

