How ERP helps implement Knowledge Management culture?
The most precious advantage of any organization is the knowledge, experience, and capability of its employees. However, it will not be possible to make the best use of this knowledge, if it resides, only in the heads of these respective employees. Every organization should, therefore, develop a culture for collecting, processing and sharing knowledge to gain a competitive advantage. Let us now see how ERP helps implement Knowledge Management culture in manufacturing industries.
What is Knowledge Management?
Knowledge management is the process of gathering important knowledge and best practices relating to people, processes, technology within the organization. Creating the relevant documentation, storing the knowledge in a central location, to be easily accessed anytime from anywhere. Sharing the right information with the right people within the organization for analyzing & learning from trends, making decisions and training employees. Using this knowledge for continuous improvement of the employees as well as the organization.
How ERP complements and helps each step of the Knowledge Management Process?
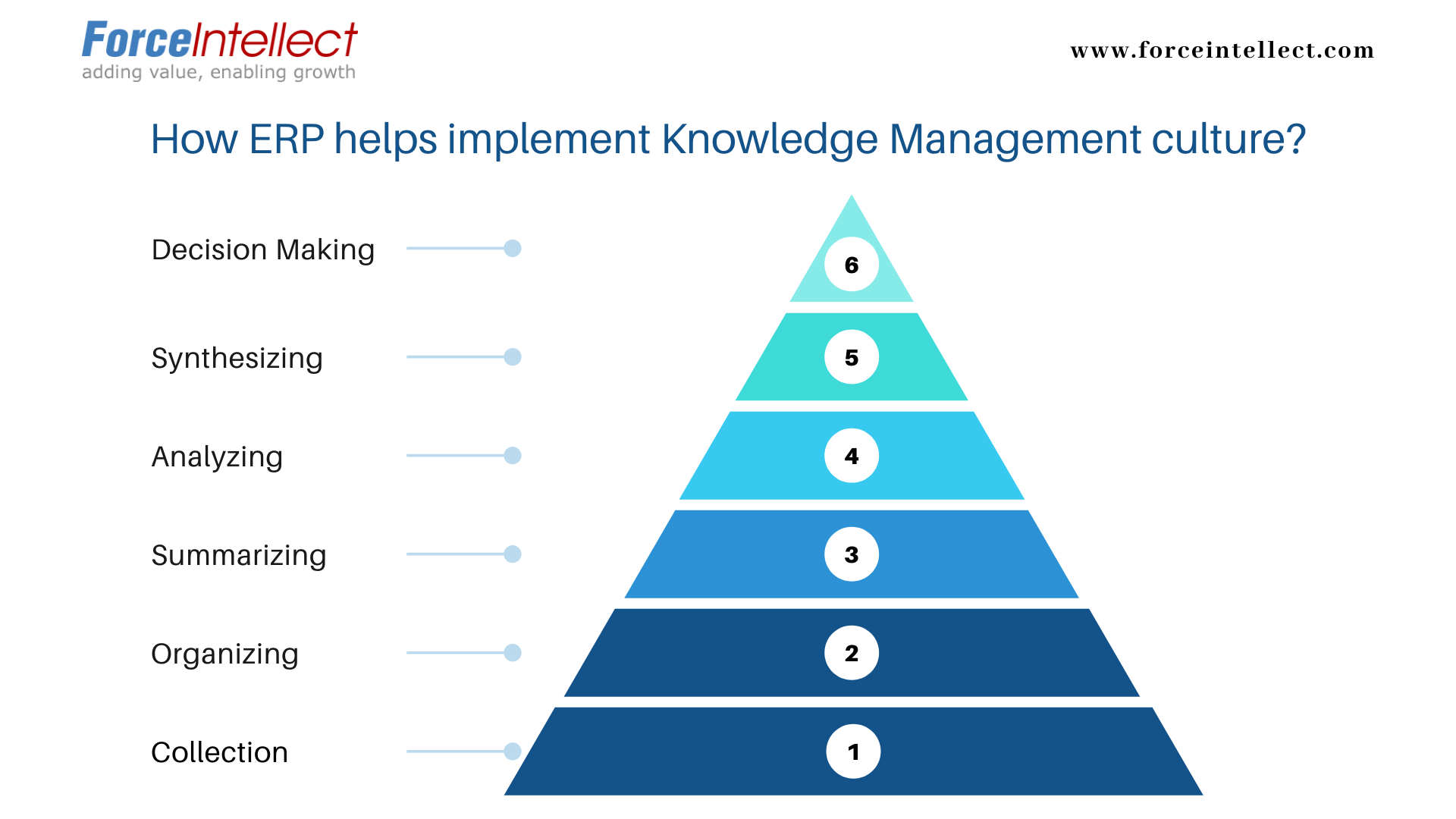
The Knowledge Management process involves six steps that have to be followed chronologically in order to successfully transforms data into knowledge. These steps are Data Collection, Data Organizing, Information Summarizing, Information Analyzing, Synthesizing, Decision Making.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software applications integrate all important processes of an organization such as planning, production, purchasing inventory, sales, marketing, finance, human resources into a centralized system. ERP automates functions, efficiently connects business verticals, provides real-time data insights across departments to make informed decisions.
While ERP gathers information across all functions, in this article, for the sake of examples and explanation we have considered the Procurement function & Inventory function throughout all the steps of knowledge management.
Data Collection:
An ERP provides standard templates, formats, and layouts for gathering data across the organization in digital format. Thus, an ERP creates a digital backbone and provides a single source of accurate data collected from different locations, departments, units, and processes of a manufacturing organization.
For e.g. ERP records all procurement-related data such as the quantity of materials required, specifications of materials, the time within which required, request for proposals, quotations received, vendor evaluation, the award of the contract is all recorded in ERP
Data Organizing:
All the data collected is then organized logically the way it is related to specific functions of the company. Rightful users are provided access based on their roles and responsibilities for enhancing department as well as companywide performance.
For e.g. All vendor-related records, contact details, items categories they supply, past transactions, their ratings, their performance is recorded in one place. Similarly, all warehouse related information such as incoming material details, material consumption details, stock availability, are organized in one place. Likewise, all pre-purchase activities such as RFQ, quotations, comparative statements can be organized in one place.
Information Summarizing:
Summarizing information involves making sense of the data and presenting it in an easy to understand formats such as graphs, charts, and more.
For e.g. ERP provides Summary of Pending Purchase Requests, Purchase Orders, Materials Received, Materials Consumption and so on
Information Analyzing:
Information that is gathered over a period of time is useful for identifying patterns, trends, and areas of improvement. ERP provides various reports relating to trends and analysis.
For e.g. Material Aging Analysis, Fast, Slow and Non-moving Items analysis, Pareto Analysis, Vendor Performance Reports, Sales Funnel Analysis, Cash Flow Fund Flow Analysis
Knowledge Synthesizing:
Once the information is carefully analyzed it can be used effectively to set benchmarks and KPIs across the organization. This will help to compare the past performance with the current and focus on continuously improving future performance.
For e.g. Procurement KPIs, Inventory KPIs, Other organizational KPIs
Decision Making:
When all the above processes have been followed meticulously it is easy to pull out facts, data, and trends in order to make informed decisions.
For. e.g. Based on past consumption data, and future forecast, a procurement manager can classify, plan and take actionable steps to optimize inventory.
What is the Importance of Knowledge Management?
An effective knowledge management process makes the most out of the intellectual assets within the company by:
- Creating proper documentation and safe-guarding knowledge within an organization
- Providing ease of availability and access to knowledge to all employees
- Enhancing employee skills & productivity by training and upgrading employees
- Building a strong base for continuous improvement in areas such as adopting new ideas for product improvement, reduce process cycle time, making data-backed decisions, etc.
- Achieving significant improvement in communication & collaboration within the organization
- Improving customer relationships by keeping track of customer requirements, their choices, preferences, & more
Summary
With this article, we have seen how knowledge management is an essential practice for an organization. We have also seen how ERP complements the knowledge gathering and knowledge management process in an organization. It helps create a culture of gathering information, analyzing information and taking fact-based, data-backed decisions that positively improves the operational performance of an organization.
Contact Us to Request a Demo of Spectrum ERP Software

